What can go in the <head> element?
The <head> tag can wrap a variety of elements that provide metadata about the document. These elements are: <title>, <meta>, <link>, <style>, <script>, and <base>. Each of these elements serves a specific purpose in defining the document’s metadata, linking to external resources, or including internal styles and scripts.
The <title> element
The <title> element is used to define the title of the document. This title is displayed in the browser’s title bar or tab, and it is also used by search engines to index the page. The content of the <title> element should be concise and descriptive.
Best SEO practices recommend that the title should be between 50 and 60 characters long, and it should include relevant keywords that describe the content of the page.
<title>My First HTML Page</title>This will show like this in the browser tab:
![]()
The title should also be different from the description, which we will discuss next, and similar, but not the same as the content of the <h1> tag.
The <meta> element
The <meta> element is used to define various metadata about the document. Think of it as key-value pairs, just that every pair is defined in a separate tag. The <meta> element can be used to define the character set, viewport settings, description, keywords, author, and other metadata.
For example, to define the character set and viewport settings, you can use the following <meta> elements:
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />The charset is important because it defines the character encoding used in the document. The UTF-8 encoding is the most widely used and supports a wide range of characters, including special characters and emojis.
The viewport settings is also very important for responsive design. It defines how the page should be displayed on different devices, such as mobile phones and tablets. The width=device-width setting ensures that the page is displayed at the width of the device’s screen, while the initial-scale=1.0 setting sets the initial zoom level to 100%.
More on responsive design in the CSS course.
The <meta> element can also be used to define the description and keywords of the page. The description is a brief summary of the page’s content, while the keywords are a list of relevant words or phrases that describe the page. For example:
<meta
name="description"
content="This is my first HTML page. It is a simple page that contains some text and images."
/>
<meta name="keywords" content="HTML, web development, frontend development" />The description should be between 50 and 160 characters long, and it should provide a concise summary of the page’s content. It is also used by search engines to display a summary of the page in search results.
The keywords are no longer relavant for SEO for the Google Search engine, but they are still used by some other search engines. It is still a good practice to include them, but don’t rely on them for SEO, as the majority of people use Google to search for content.
The author meta tag is used to define the author of the document. It is not as important as the title and description, but it can be useful for attribution purposes. For example:
<meta name="author" content="John Doe" /> The <base> element
It is used to define the base URL for all relative URLs in the document. This is useful if you have links or resources that are relative to a specific URL. For example:
<!-- Your domain -->
<base href="https://example.com/" /> The <link> element
It is used to link to external resources, such as stylesheets or icons. For example, to link to a stylesheet, you can use the following <link> element:
<!-- The href attribute could be relative or absolute -->
<!-- It could also rely on the <base> tag -->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="styles.css" />Stylesheet is the other name for a CSS file.
It could also be used to link to a favicon, which is the small icon that appears in the browser tab or bookmarks. For example:
<link rel="icon" href="favicon.ico" type="image/x-icon" />The icon on the left of the title is the favicon.
![]()
And yes… favicon stands for “favorite icon”. In the 1990s, when IE was still the king of browsers, there was a feature called “favorites”, which allowed users to save their favorite websites. There was the need for visual distinction, so IE team instructed developers to create a small icon and put in inside the root of the website, and it was called “favicon.ico” from “favorite icon”. The name stuck, and now it is used by all browsers. The more you know!
The <style> element
The <style> element is used to include internal CSS styles in the document. This is useful for small styles that are specific to the page and do not require an external stylesheet. For example:
<style>
body {
background-color: #f0f0f0;
color: #333;
}
</style>These styles are just like the inline styles. Their scope is just this document, and they are not applied to other pages. They are also not as powerful as external stylesheets, but they can be useful for small styles that are specific to the page.
The <script> element
The <script> element is used to include JavaScript code in the document. This is useful for adding interactivity and dynamic behavior to the page. For example:
<script>
console.log('Hello, world!')
</script>JavaScript is the language that powers the web, and it is used to create dynamic and interactive web pages. It is a powerful language that can be used to manipulate the DOM, handle events, and perform various tasks on the page. JavaScript is not covered in this course, but it is an essential part of web development, and you will learn more about it in the JavaScript course.
Open Graph
In simple words, Open Graph is the protocol, that allows web pages to be shared with images. Every time you share a link on social media, in a messaging app or just paste in your notes - the preview you get is generated using Open Graph metadata. It is a set of <meta> tags that you can add to your HTML document to define how the page should be displayed when shared on social media.
For example, to define the title, description, and image of the page, you can use the following <meta> elements:
<meta
property="og:title"
content="How to add a Read more button to a block of HTML in React"
/>
<meta
property="og:description"
content="Adding a read more button that to a block of text, which does not break html tags and is not show if te..."
/>
<meta property="og:image" content="https://example.com/image.jpg" />This is how this link would look like when shared on a messaging app or social media:
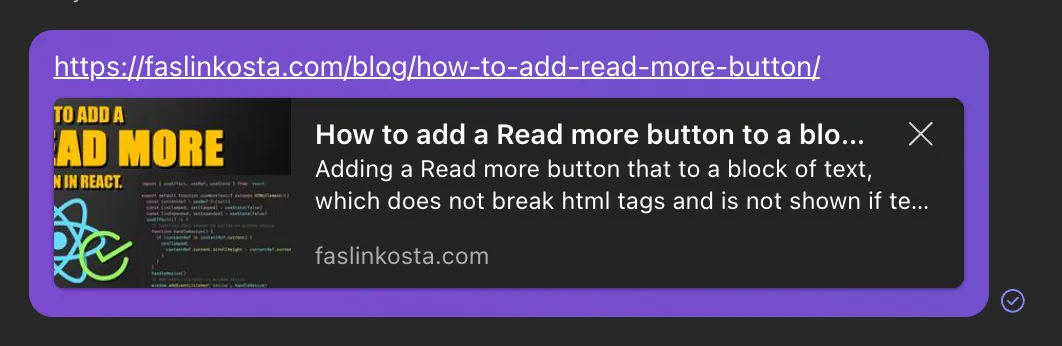

And remember when I sait that the title should be 50 to 60 characters long? Well, the Open Graph title should be between 60 and 90 characters long, and the description should be between 100 and 200 characters long. This is because social media platforms have different requirements for the length of the title and description.
Despite of that, mine gets cut! The Audacity…
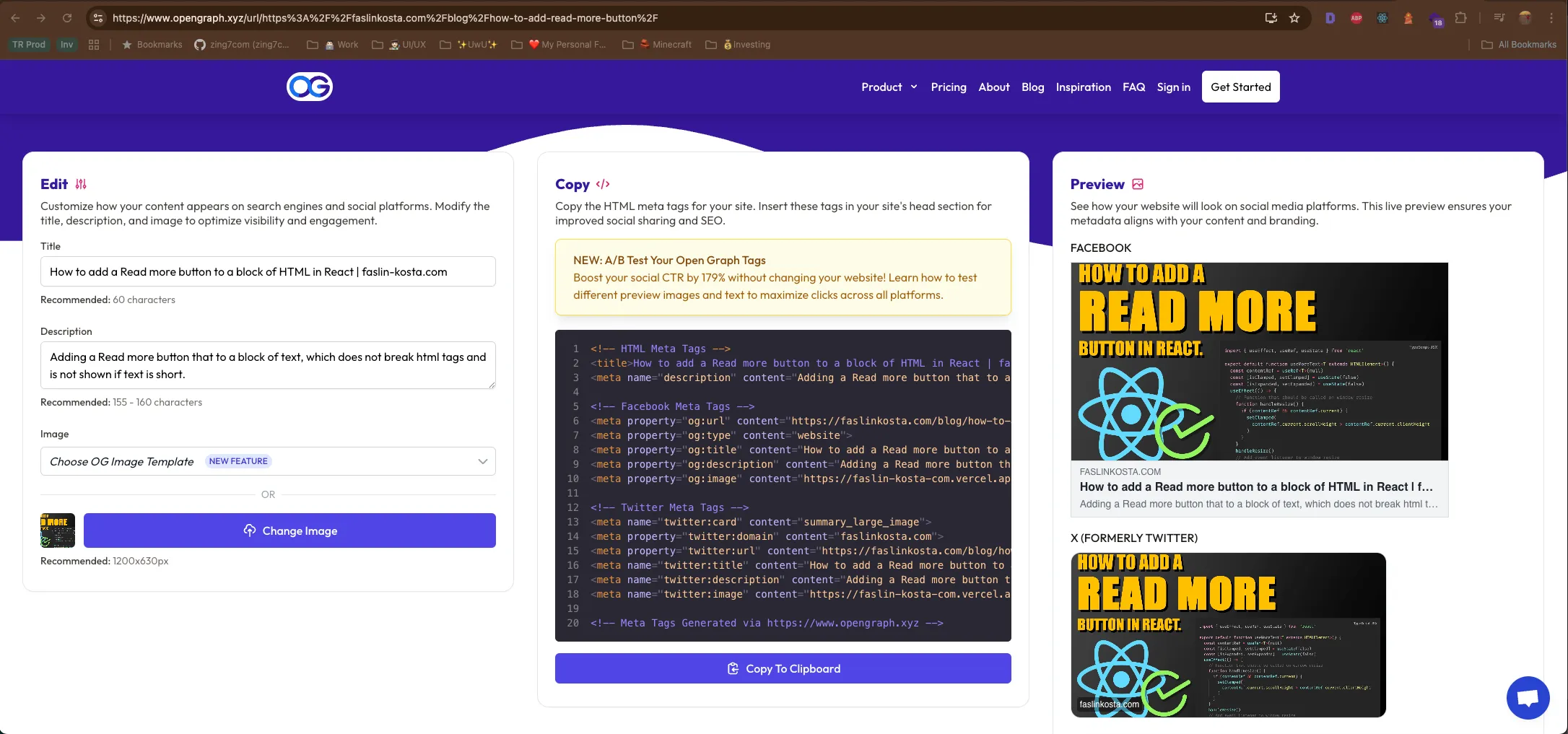
Always check how your page looks like when shared on social media. At the time of writing this, you can use the The open graph debugger to see how your page will look like when shared on Social media. It will also show you any errors or warnings related to the Open Graph metadata and give you a form to change the title, image and description to see how it will look like when shared. It will also give you the HTML code that you can copy and paste into your page. Kids these days have it easy!
Conclusion
- The
<head>element is the wrapper for metadata about the document. - The
<title>element defines the title of the document, which is displayed in the browser’s title bar or tab. - The
<meta>element is used to define various metadata about the document, such as character set, viewport settings, description, keywords, and author. - The
<base>element defines the base URL for all relative URLs in the document. - The
<link>element is used to link to external resources, such as stylesheets or icons. - The
<style>element is used to include internal CSS styles in the document. - The
<script>element is used to include JavaScript code in the document.


